Do you know the right particle counter you need when it comes to monitoring environments, communications, monitoring purposes, desired flow rate, and particle sizes? Selecting an airborne particle counter starts with knowledge of what you need, then finding the right solution.
This application note will help you select an airborne particle counter by helping you:
- Understand how to monitor your clean environments in accordance with ISO standards
- Solve your contamination control issues
- Learn how to improve your processes to reduce sources of particulate contamination
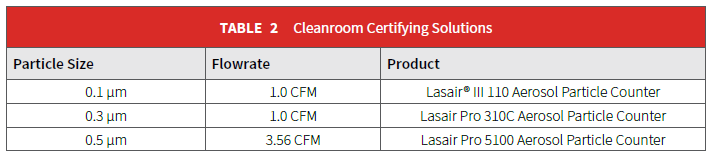
For example, monitoring a cleanroom in accordance with ISO cleanroom classifications requires the particle counter’s maximum concentration specification to exceed ISO limits. Solutions to aid in attaining cleanroom certification are listed in Table 2.
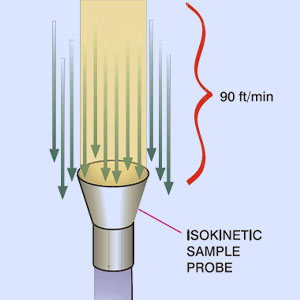
There are features available in airborne particle counters to best address the various applications and needs of the customers. The right particle counter will depend on the monitoring environment, communications, monitoring purposes, desired flow rate, and particle size you choose to monitor. This article will identify the various features available and help identify which are relevant to your application. Pharmaceutical manufacturing has special monitoring requirements that are not completely addressed here.
Terminology
All airborne particle counters sample air at a specified volumetric flowrate which is defined as the speed of air being pulled through the particle counter. The flowrate units are usually in cubic-feet-per-minute (CFM) or liters-per-minute (LPM). Particle counters are calibrated to sample at their specified flowrates, and sizing accuracy is dependent on that flowrate.
To meet classification standards, particle counters sample defined volumes of air which provide qualifiable, statistical significance to particle count data.
This paper covers:
- Standards and Certification
- Frequent or Continuous Cleanroom Monitoring
- Monitoring Locations
- Minienvironments
- Filter and Valve Testing
- Lab Testing
- Harsh Environments
- Counting Particles in Gases